光学 精密工程
2023, 31(11): 1581
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical System Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
We implemented a stitching swing arm profilometer (SSAP) test for the inner and outer regions of a large aspheric surface with a short arm. The SSAP was more capable of improving sampling density of surface and was less sensitive to system error, like vibration noise and air-table noise. Firstly, a calculation model was built to evaluate the sampling density of the SSAP test. Then, sensitivity to system noise was tested when different lengths of arm were used. At the end, an experiment on a 3 m diameter aspheric mirror was implemented, where test efficiency was promoted, and high sampling density was achieved.
220.1250 Aspherics 220.4840 Testing 120.3940 Metrology 120.4640 Optical instruments Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 112201
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
提出了一种基于哈特曼原理子口径斜率扫描再重构波面的检测方式, 研究了一种解决大口径光学系统不同俯仰角下的像质评价的方法。该方法无需同等口径标准镜, 通过扫描方式获取波面信息。采用光学软件与数学分析软件通过DDE接口连接进行计算机联合仿真的方式进行探究, 仿真光学系统采用主镜Φ720 mm, 次镜Φ100 mm的卡塞-格林系统来验证该方法的可行性, 利用随机误差注入及多次扫描平均的方法进行了该检测方式中重构波面精度的研究; 系统探究了光斑中心提取误差、子口径定位误差、子口径倾斜误差对于该检测方法重构波面精度的影响。给出了该方法仿真结果与光学软件仿真结果的对比, 并获取了误差注入时各误差与重构波面精度的物理模型。
波面检测 哈特曼原理 大口径光学系统 斜率扫描 wavefront detection Hartmann principle large aperture optical system slope scanning 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(8): 0813003
中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 中国科学院光学系统先进制造技术重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
为满足空间遥感光学系统结构紧凑、体积小以及高分辨率的需求, 提出了一种长焦距紧凑型光学系统的设计方法。基于高斯光学和初级像差理论, 创建了同轴四反射镜系统的初始结构, 通过视场偏置的方法避免二次遮拦。对设计的大口径超长焦距同轴偏视场四反射光学系统进行优化, 系统口径1 800 mm, 有效焦距25 000 mm, 全视场角1°×0.1°。设计结果表明, 系统设计波像差优于λ/50(λ=632.8 nm), 全视场相对畸变小于0.4%, 光学筒长仅为有效焦距的1/10, 结构简单紧凑, 像质接近衍射极限, 对大口径超长焦距空间遥感光学系统的设计具有一定的借鉴作用。
光学系统设计 四反射镜系统 高斯光学 像差理论 大口径 optical system design four-mirror system Gaussian optics aberration theory large aperture
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 中国科学院光学先进制造技术重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京100049
为了确定摆臂式轮廓检测大口径离轴非球面采用不同扫描线数时系统检测误差的敏感性, 文中提出采用蒙特卡洛方法, 建立了仿真分析的模型。对母线条数分别为8~120条的模式进行模拟检测, 对系统噪声引入的面形误差进行Zernike多项式项拟合, 统计分析得母线条数为8~39条时, 系统噪声引入的低阶项检测误差随母线条数的增加而迅速降低; 母线条数为40~70条时, 引入低阶项检测误差降低缓慢; 71~120条时, 引入的低阶项检测误差几乎保持不变。结合实例, 对一口径1 500 mm的离轴非球面反射镜进行实验, 分别采用36条、72条和96条母线进行面形检测。36条母线检测误差相对较大, 检测结果为7.73 μm PV和0.68 μm RMS;72条母线和96条母线检测结果十分接近, 分别为5.755 μm PV, 0.568 μm RMS和 5.612 μm PV, 0.569 μm RMS。验证了仿真分析结果的准确性, 为摆臂式轮廓检测大口径离轴非球面中母线条数的优化选择提供了理论指导。
大口径 离轴非球面 摆臂式轮廓检测 仿真分析 large aperture off-axis aspherics SAP test simulation analysis 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(2): 0217003
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 中国科学院光学系统先进制造技术重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
为满足空间成像领域对大口径、轻量化、高衍射效率光学衍射元件的需求, 研究了薄膜衍射元件微结构设计及制作工艺。应用Zemax光学软件设计了320 mm口径, F/#100的四台阶薄膜菲涅尔衍射元件, 并利用Matlab软件将连续位相结构转化为离散化台阶分布。研究了薄膜菲涅尔衍射元件的制作技术, 选用透明聚酰亚胺薄膜作为基底材料, 以石英玻璃作为复制模板, 通过多次旋涂的方式实现了厚度为20 μm的衍射薄膜制作。应用Solidworks软件设计并加工薄膜支撑装置。测量复制基板及薄膜对应区域的微结构, 实验结果表明条纹线宽转移偏差小于1.3%, 台阶深度偏差小于8.6%。搭建光路测试在波长632.8 nm处衍射效率平均值为71.5%, 达到了理论值的88%。实验结果表明, 制作的薄膜重量轻, 复制精度高, 并且具有高衍射效率, 满足空间望远镜的应用要求。
大口径 菲涅尔衍射元件 聚合物薄膜 聚酰亚胺 衍射效率 large aperture Fresnel diffractive element polymer membrane polyimide diffraction efficiency 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(9): 0920001
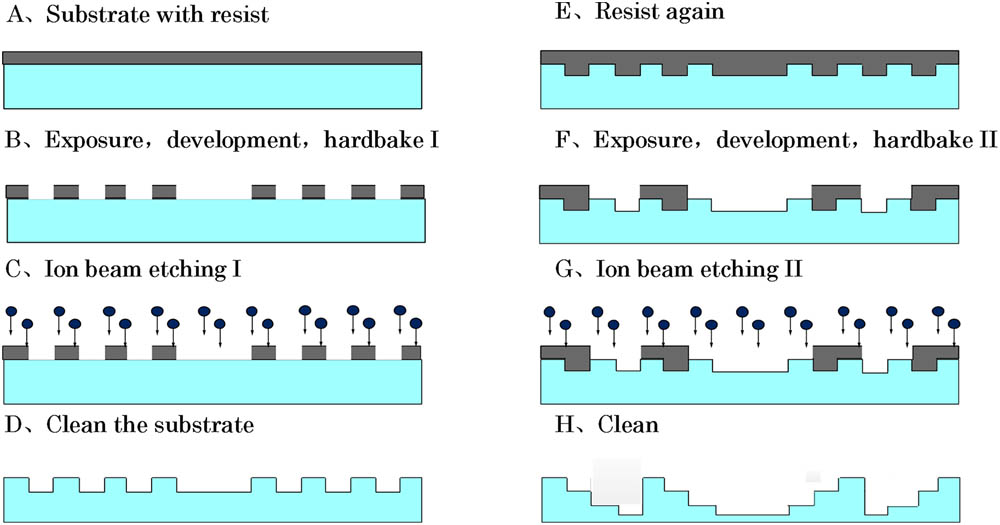
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optical System Advanced Manufacturing Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The demand for space-borne telescopes with an aperture of 20 m is forcing the development of large diameter diffractive Fresnel zone lenses (FZLs) on membranes. However, due to the fabrication errors of multi-level microstructures, the real diffraction efficiency is always significantly smaller than the theoretical value. In this Letter, the effects of a set of fabrication errors on the diffraction efficiency for a diffractive membrane are studied. In order to verify the proposed models, a 4-level membrane FZL with a diameter of 320 mm is fabricated. The fabrication errors of the membrane FZL are measured, and its diffraction efficiency in the +1 order is also tested. The results show that the tested diffraction efficiency is very close to the calculated value based on the proposed models. It is expected that the present work could play a theoretical guiding role in the future development of space-borne diffractive telescopes.
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 160.5470 Polymers 120.4610 Optical fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120501
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,中国科学院光学系统先进制造技术重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
为了满足大口径反射镜研磨阶段的面形检测需求,分析了激光跟踪仪测角误差的来源,提出了一种基于S多项式拟合的矫正测角误差的方法,该矫正方法能有效克服采样位置误差和随机误差带来的影响。针对不同频段测角误差,提出母线和米字格采样法,其中母线采样法对10%以内的标定实验随机误差有较好的抑制作用。矫正方法的可行性得以验证,从而为进一步实验提供了理论基础。
光学设计 激光跟踪仪 角度误差补偿 大口径非球面镜 多项式拟合 中国激光
2016, 43(11): 1104003
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院光学系统先进制造技术重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
阐述了基于相位差异(PD)的波前传感技术的基本原理;仿真分析了PD技术的噪声适应性及探测器离焦误差对精度的影响;利用PD技术的波前传感结果分别辅助装调了离轴、同轴三反光学系统,并分别将多视场的波前图与干涉检验的结果进行对比。实验结果表明,利用PD技术可实现三反光学系统的波前传感及辅助装调。与干涉检验的结果相比,波前传感结果的RMS偏差均优于0.02λ,检测精度满足工程需求。
成像系统 相位差异 波前传感 离轴三反光学系统 同轴三反光学系统 辅助装调

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical System Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
Null lenses are always used to test large convex aspheric mirrors. For large convex aspheric mirrors with large deviate wavefronts from the aspheric wavefront to its best sphere wavefront, a traditional null lens composed of a flat and a sphere cannot be used to test. An aspheric null lens needs to be designed and manufactured to test a large convex aspheric mirror with a large deviate wavefront. Another traditional null lens is used to guide the manufacture of the aspheric null lens. The accuracy and feasibility of the aspheric null lens are unknown and should be tested by a high precision computer-generated hologram (CGH). In the article, we introduce the principle of a null lens, designed an aspheric null lens to test a Φ338 mm aspheric SIC mirror whose radius of curvature is 1024 mm, the deviate wavefront from the aspheric wavefront to its best fit sphere wavefront is 66.5728λ PV (λ=632.8 nm). The result of the aspheric null lens that is tested by a CGH is 0.018λ RMS and satisfies the need of accuracy. The test result of the aspheric mirror is 0.030λ RMS.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S21203





